Translate this page into:
Puzzling papular eruptions on an old scar
[To cite: Das P, Gupta A, Barui S, Singh GK, Bahuguna A, Sapra D, et al. Puzzling papular eruptions on an old scar. Natl Med J India 2023;36:275–6. DOI: 10.25259/NMJI_652_22]
A 32-year-old man, who sustained an abrasion on his right cheek 7 years ago, presented with skin-coloured asymptomatic papules over the scar for 3 months. Dermatological examination revealed non-tender, grouped skin-coloured papules over erstwhile abrasion on the right malar prominence (Fig. 1a). Dermoscopy of the lesions showed linear to stellate scarred areas on translucent erythematous to brown homogeneous background (Fig. 1b). Skin biopsy revealed non-necrotizing epitheloid granulomas with Langhans giant cells with minimal lymphocytic cuffing and asteroid bodies suggestive of sarcoidosis (Figs 2a, 2b). The patient did not have any symptoms of pulmonary sarcoidosis such as breathlessness, cough, haemoptysis and weight loss. CT chest revealed multiple discrete to confluent pleural, peri-lymphatic and fissural nodules in bilateral lung fields (Fig. 3a); with multiple enlarged discrete lymph nodes in pre/para-tracheal, pre-vascular, pre/sub-carinal and bilateral hila; the largest measured 23 mm in the right para-tracheal region (Figs 3b, 3c). Trans-bronchial biopsy showed non-caseating granuloma suggestive of sarcoidosis and was negative for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The patient was diagnosed as a case of cutaneous as well as pulmonary sarcoidosis and was started on systemic steroids and is on follow-up.

- (a) Unilateral involvement of the right upper malar area in the form of skin-coloured grouped papules; (b) dermoscopy shows white areas of stellate and linear scarring (yellow arrows) on the background of brown to erythematous homogeneous areas (green stars) (IDS-1100, ×10)
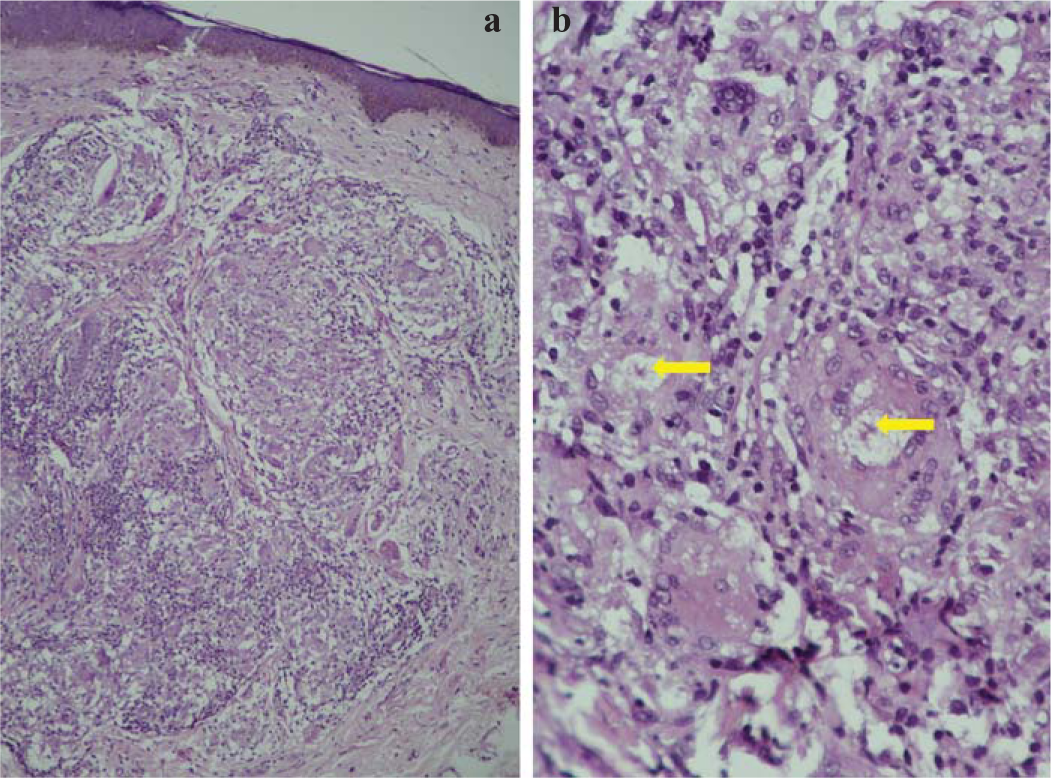
- (a) Biopsy shows thin epidermis with flattening of rete-ridges. The underlying dermis is packed with many non-necrotizing granulomas (H&E, 20×); (b) these granulomas are composed of epitheloid histiocytes with minimal lymphocytic cuffing. Some of the granulomas also show asteroid bodies (yellow arrows; H&E, 40×)
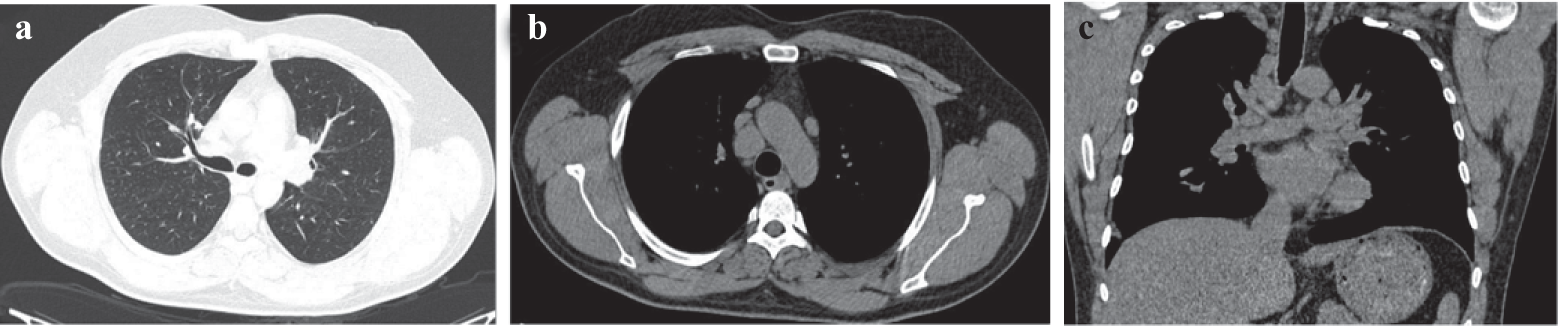
- (a) NCCT chest shows multiple well-defined discrete sub-centimetre peri-lymphatic nodules with upper lobar predominance; (b) axial NCCT image shows multiple discrete, enlarged right paratracheal lymph node; (c) coronal NCCT image shows multiple discrete, enlarged right paratracheal and hilar lymph nodes
Around 10%–38% of patients with systemic disease present with cutaneous sarcoidosis.1 The reported latency period of scar sarcoidosis before its reactivation in old cutaneous scars is between 6 months and 59 years.2 Scar sarcoidosis may precede or coincide with systemic sarcoidosis or may be a sign of relapse of systemic disease activity.3 Reactivation of old scars is believed to be highly specific for sarcoidosis and an approachable site of biopsy from skin obviates the need for more invasive procedures in the form of trans-bronchial biopsies.4
Conflicts of interest
None declared
References
- Cutaneous sarcoidosis: differential diagnosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:276-87.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scar sarcoidosis with systemic involvement after blepharoplasty. Int J Ophthalmol. 2021;14:1288-90.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disseminated scar sarcoidosis may predict pulmonary involvement in sarcoidosis. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2013;22:71-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Scar sarcoidosis: 11 patients with variable clinical features and invariable pulmonary involvement. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:826-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




