Translate this page into:
Wild bee sting causing venous thromboembolism
[To cite: Zhang L, Ma Y. Wild bee sting causing venous thromboembolism. Natl Med J India 2024;37:294. DOI: 10.25259/NMJI_883_2023]
A 35-year-old man with no medical history was sent to the emergency department of our hospital 3 days after his left lower limb was stung by a wild bee during a field trip. The patient’s left lower limb swelling, and redness had increased, accompanied by chest tightness. Physical examination showed that compared with the opposite thigh, his left lower limb was swollen, left leg was painful and left thigh diameter had increased by 3 cm (Fig. 1). There was a moist rale in the lung on auscultation. Doppler ultrasound confirmed the presence of iliofemoral vein thrombosis in the left lower limb of the patient, and CT scan of the chest also confirmed the presence of pulmonary embolism (Fig. 2).

- Physical examination showed a swollen left lower limb
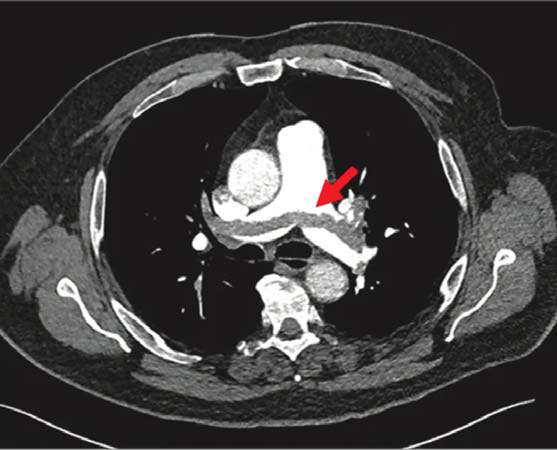
- CT scan of the chest confirmed pulmonary embolism (Red arrow)
An allergic reaction to insect bites is often caused by bees.1 The sensitivity of normal people to bee venom is 15%–25%.2 However, since the patient had no other symptoms and no other factors to induce thrombosis, this strongly suggested deep venous thrombosis caused by a bee sting, leading to pulmonary embolism. Bee stings can cause cerebral infarction and thrombosis of other arteries, such as coronary artery or abdominal aorta.3–5 However, venous thromboembolism after bee sting is very rare.
Conflicts of interest
None declared
References
- Prevalence of allergy to hymenoptera stings. Allergy Proc. 1990;11:29-32.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anaphylaxis from wasp stings inducing coronary thrombus. Case Rep Cardiol. 2012;2012:701753.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descending aortic thrombosis and cerebral infarction after massive wasp stings. Am J Med. 2004;116:567-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilateral cavernous sinus syndrome and bilateral cerebral infarcts: A rare combination after wasp sting. J Neurol Sci. 2011;301:104-6.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




